What is a good hardness level for water softener
Whether you’re managing water quality in your home or running a large-scale industrial operation, understanding water hardness is essential. Hard water affects everything from household appliances to complex industrial machinery, making regular water hardness testing a crucial step in maintaining efficiency, reducing maintenance costs, and extending equipment life.

Understanding water hardness
First things first: what exactly is water hardness? In simple terms, it refers to the concentration of minerals—primarily calcium and magnesium—in your water. High concentrations result in “hard water.” On the other hand, low concentrations mean “soft water.”
Water hardness is commonly measured in parts per million (ppm) of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), grains per gallon (gpg), or degrees of hardness (French °f or German °dH). Here’s a general guide for classifying water hardness:
- Very Soft Water: 0 to 50 ppm
- Soft Water: 50 to 100 ppm
- Slightly Hard Water: 100 to 150 ppm
- Hard: 150 to 200 ppm
- Very hard: Over 200 ppm
The ideal hardness range
If you’re wondering about the ideal hardness range for your water, it falls between soft and moderately hard water. Having slightly hard water means you’ll still reap some mineral benefits without suffering from common hard water problems.
A consensus among experts suggests that an ideal setting for a water softener should aim to reduce hardness to around 80-100 ppm CaCO3 or approximately. This ensures balanced water that isn’t too soft or excessively hard.
For effective boiler operation, total hardness (TH) should be controlled:
- TH for Heating Water: Less than 100 ppm to avoid corrosiveness and scaling.
- TH for Make-Up Water: Less than 50 ppm
Consequences of hard water
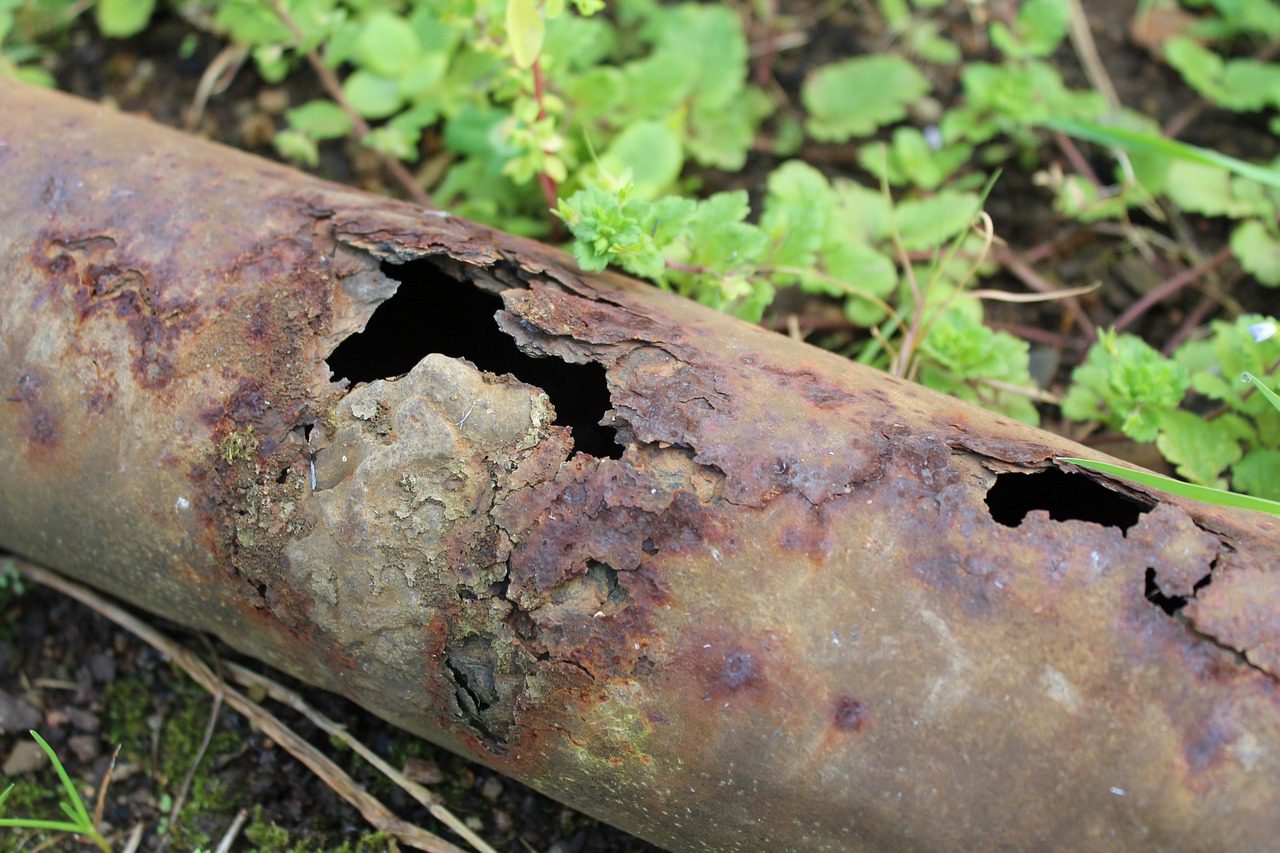
For households, hard water can result in unsightly deposits on faucets and dishes, poor soap lathering, and skin irritation. For industries—such as boiler rooms, manufacturing plants, and water softener systems—hard water can lead to significant scaling, which decreases heat transfer efficiency, raises energy costs, and damages critical machinery.
Why not too soft?
While very soft water is often considered ideal due to its numerous benefits, including optimal appliance performance and better soap lathering, it’s not universally advisable. Extremely soft water tends to be more aggressive and may corrode metal piping more quickly, promoting the formation of leaks.
Moreover, the lack of minerals in very soft water can sometimes result in an unpleasant taste. That’s another reason why moderately soft water levels strike the right balance.
The role of water hardness in industrial processes
Water is a cornerstone of industrial processes, whether as a coolant, cleaning agent, or ingredient. Hard water can cause scale build-up in machinery, reducing efficiency and increasing the risk of costly downtime. For instance:
- Boilers and Heat Exchangers: Excess minerals in hard water precipitate under heat, forming scales that insulate heat transfer surfaces. This leads to higher energy consumption and potential overheating.
- Food and Beverage Production: Hard water can alter the taste and consistency of products, making water treatment a key step in maintaining quality standards.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Extremely soft water is often required to prevent mineral contamination during production, necessitating precise control of water hardness levels.
Tools for measuring water hardness
You might now wonder how to measure your home’s water hardness. Luckily, various tools are available for this purpose.
Homeowners can easily test water hardness using test strips or home water test kits:
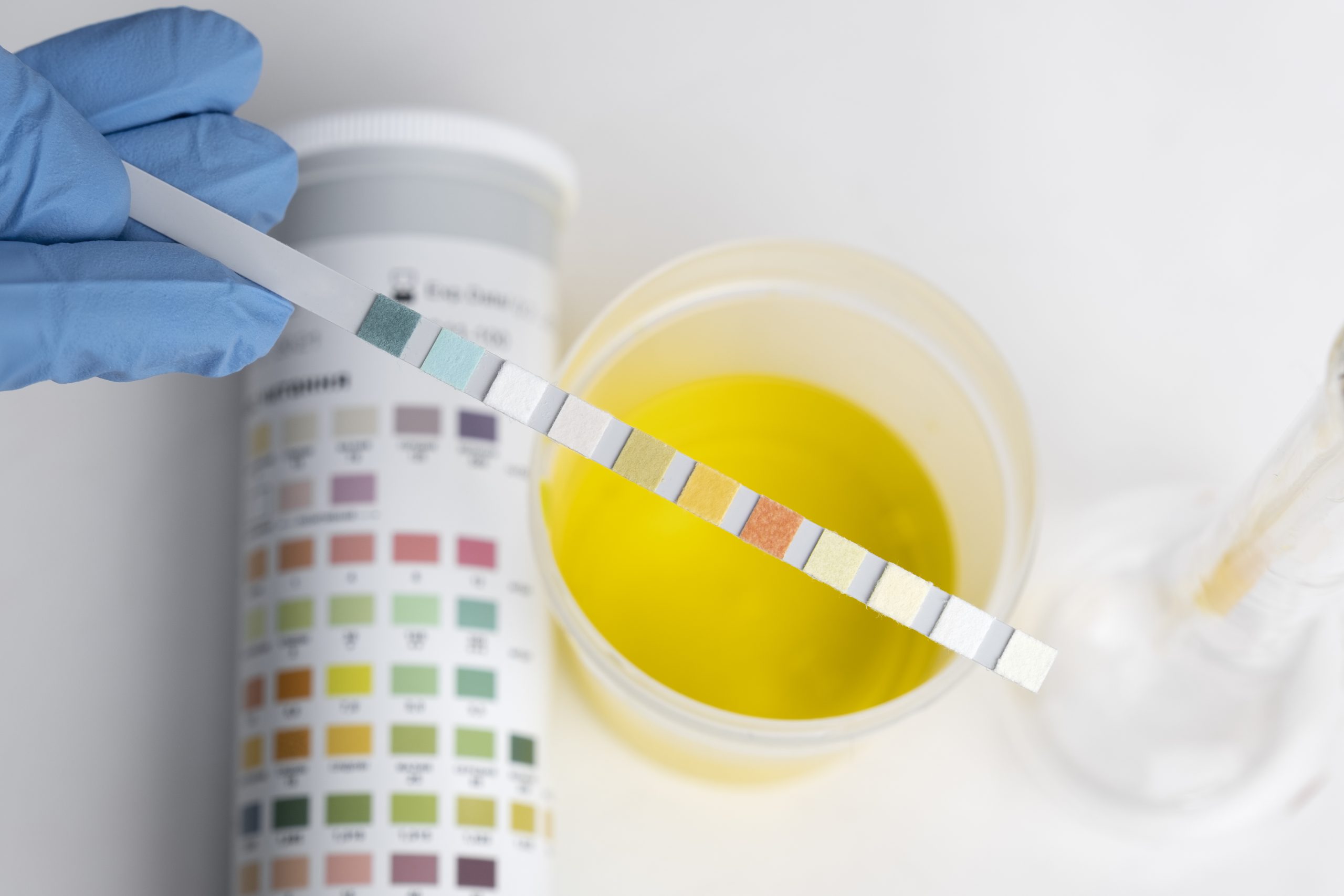
- Water Test Strips: These are a simple, quick way to measure water hardness. Dip a strip into a water sample, wait a few seconds, and compare the color change to the provided chart. While these strips give a general indication of water hardness, they may not be precise enough for critical applications.
- Drop Test Kits: These kits, available from Aqualabo, provide more accurate readings through dropwise titration. A reagent is added to the water sample until a color change indicates the hardness level. For homeowners seeking reliable, repeatable results, drop test kits offer a step up from test strips.
For industrial systems, precise and frequent monitoring is essential. Water hardness affects the operational efficiency of boilers, cooling towers, and other critical systems. Scale build-up in these environments can lead to downtime, energy waste, and costly repairs.
To avoid these issues, industries rely on drop test kits and burette titration kits:
- Drop Test Kits: Aqualabo’s drop test kits are designed for frequent, quick analysis. Using a reagent, the water sample changes color when the hardness is detected, providing a simple and effective solution for testing water hardness in real-time.
- Burette Titration Kits: For industrial environments that require higher accuracy and efficiency, burette titration kits offer more precise control over reagent volumes, enabling detailed analysis. These systems are ideal for industries that need to conduct large-scale testing of water hardness, such as water softener manufacturers, boiler room operators, and food production facilities.
Solutions for Managing Water Hardness
Both homeowners and industrial users can take action to manage water hardness effectively.
Home Solutions
For homeowners, a water softener is the most effective long-term solution for hard water. Water softeners use a process called ion exchange to replace hardness-causing minerals with sodium ions, preventing scale build-up and protecting appliances.
Industrial Solutions
Industries need robust solutions to handle the high demands of industrial systems.
Potential solutions for industrial applications include :
- Chemical Softening: Installing a chemical softening system on the municipal water supply to remove calcium and magnesium, which can then be disposed of through wastewater.
- Physical Softening: Implementing physical anti-scaling systems, such as magnetic, electronic, or catalytic devices, to mitigate scale formation without chemical treatment.
Maintenance tips for your water softener
Like any other device, a water softener requires regular upkeep to function efficiently. An overlooked aspect of maintaining a water softener involves periodic inspections and timely brine tank refill. Without sufficient salt, the system won’t work effectively.
Regular inspections
Ensuring your system remains in top condition includes regularly checking for salt bridging (when solidified salt causes blockages), inspecting valves, and confirming the proper functionality of electrical components. Ideally, these checks should coincide with routine house maintenance schedules.
Brine tank refills
It’s vital to keep an eye on the brine tank’s salt levels. When they drop below half, it’s time for a refill. The frequency will depend on your water usage and the initial water hardness level. Consistent refilling prevents the resin bed from failing, ensuring soft water flows through your pipes all year round.
Common issues and troubleshooting
Water softeners are sophisticated machines, but like any household equipment, they aren’t immune to glitches. Being aware of common problems and solutions can save time and money in the long run.
Salt bridges
One frequent issue that arises is salt bridging. Due to high humidity or using the wrong type of salt, hardened bridges form inside the brine tank, obstructing normal operations. Breaking up these formations with a broom handle usually resolves the problem.
Resin bed fouling
Another challenge is resin bed fouling, where iron, manganese, or organic compounds clog the resin beads, reducing their efficiency. Employing specialized cleaners or products designed for iron removal can extend the life of your resin bed while sustaining optimal performance.
Economical and environmental benefits
Investing in a well-maintained water softener contributes more than just improving household conveniences. There are considerable economical and environmental advantages tied to managing the correct water hardness level.
- Extended appliance lifespan : By minimizing scale build-up in appliances like washing machines, dishwashers, and water heaters, softer water helps these devices function efficiently longer. This reduces household expenses over time, thanks to fewer repairs and replacements.
- Energy savings : Unnecessary energy consumption often results from scaled-up appliances struggling to perform optimally. With softened water, these appliances require less energy, leading to lower utility bills. Plus, homes utilizing moderately hard water witness improved thermal efficiency in boilers and heaters.
Final words
Water hardness is an important factor for both households and industries. Homeowners benefit from regular water hardness checks to protect appliances and maintain water quality, while industrial users must monitor water hardness carefully to prevent equipment damage and inefficiencies.
By using Aqualabo’s drop test kits or burette titration kits, you can ensure precise, reliable results that help maintain your systems, whether at home or in an industrial environment. Taking control of your home’s water hardness level offers ample rewards, from extending the lifespan of plumbing systems to providing more pleasant bath times.
Start by determining your current hardness level. Once you have the data, adjust your water softener setting accordingly for optimal results. Do not overlook regular maintenance practices, particularly consistent brine tank refill routines, to keep your system working smoothly. Enjoy the myriad benefits of moderately soft water and say goodbye to those pesky lime deposits forever!