
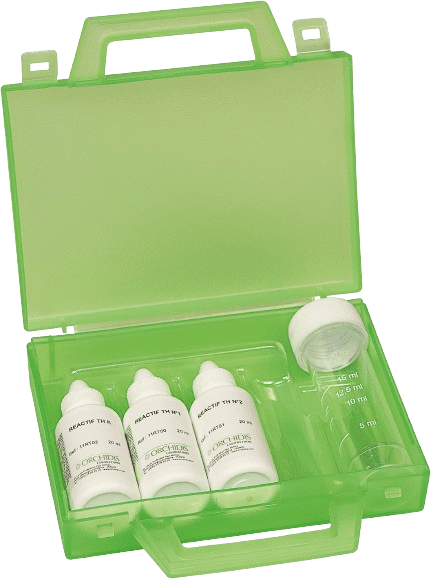
Hardness test kit for all types of water (3 bottles) 1 drop = 2°F
Ref: 1KT001
Range: 2 to 60°F
Number of tests: 40
Discover our rapid and reliable test kits for analyzing water hardness. Available as kits and portable cases for occasional or domestic use, as well as large scale reagents used in laboratory burette methods for frequent testing in an industrial environment.
Accurate measurement of water hardness is essential to prevent lime deposits and ensure the longevity of machinery and pipework, while improving the energy efficiency of processes and the quality of circulating water.
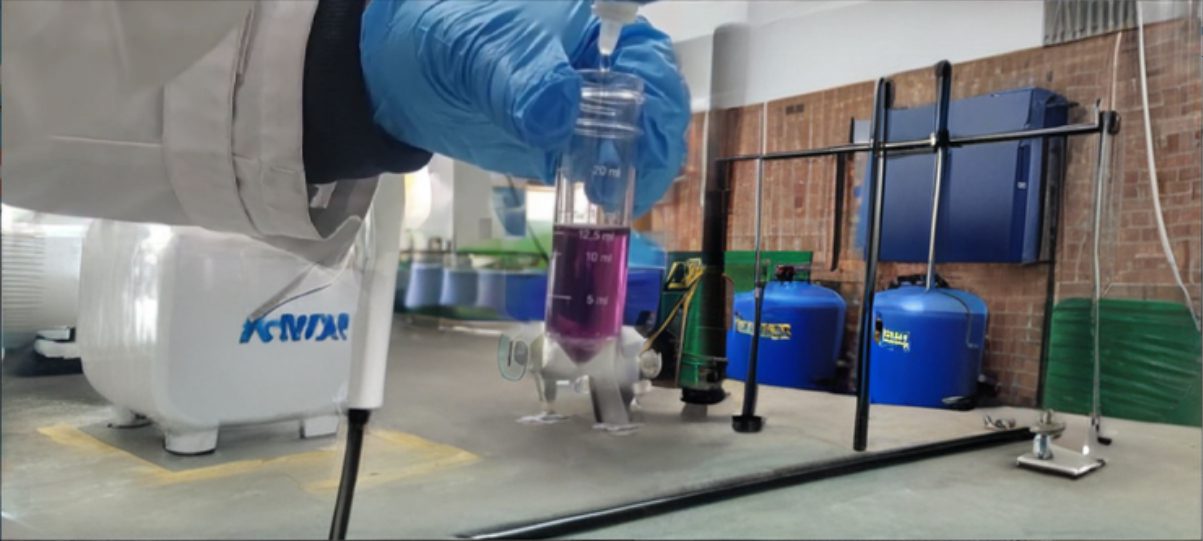

“Explore our dropper water hardness test kits, a quick and easy way to assess water hardness, suitable for different water types.
The dropper titration method changes the color of the sample from red to blue at the equivalence point. The number of drops needed for the color to change represents the hardness concentration.”

Ref: 1KT001
Range: 2 to 60°F
Number of tests: 40
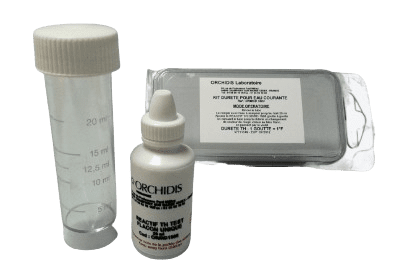
Ref: 1KT005
Range: 0.05 to 2°F
Number of tests: 20 to 40
Ref: ORMCD1003
Range: 1 to 60°F
Number of tests: 20 to 40
Optional cardboard packaging available
Optional 30 ml bottle available
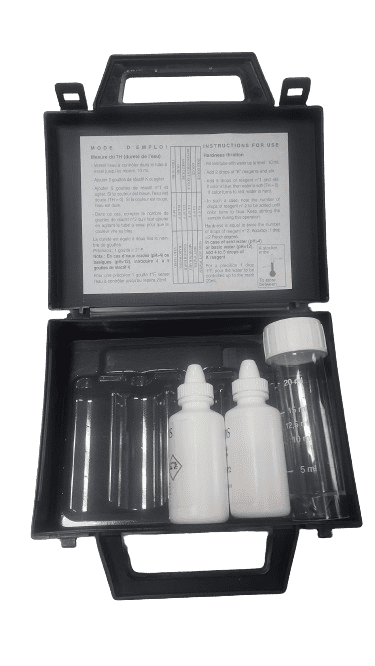
Ref: 1KT004
Range: 2 to 60°F
Number of tests: 40
Burette dropper titration methods to determine water hardness concentration offer a greater titrant solution storage capacity, thereby increasing the number of tests and speed with which they can be performed.
Optional: burette with a stand or burette with bottle pressure fill.

Burette titration methods offer a greater titrant solution storage capacity, thereby increasing the number of tests and speed with which they can be performed.
Learn moreMulti or single parameter analysis cases can accommodate dropper, burette, color scale methods and pocket testers. Known for their portability, comprehensiveness, and sturdiness, each case comes with instructions and is fully equipped to carry out the analyses.
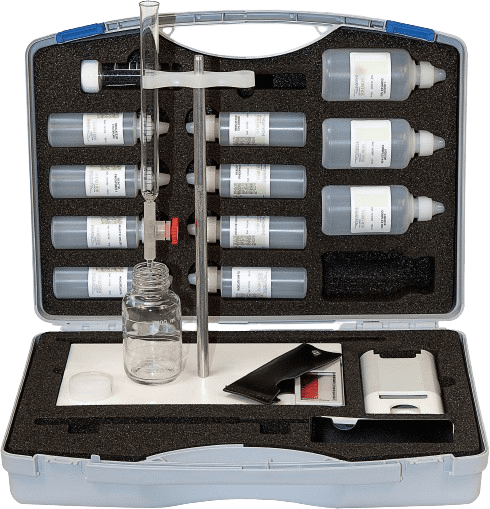
Adjustable hardness test case: dropper, burette of your choice. Additional tests can be included according to your specific needs.
Learn more“Discover our water softener maintenance option. The demonstration case includes a mini softener and hardness tests, providing a comprehensive operating package.
For optimal maintenance, our resin cleaner simplifies regeneration and disinfection. It is available in various sizes.”

Available in a range of sizes, it is designed to regenerate and disinfect water softener resins. A key step for effective system maintenance.
Learn more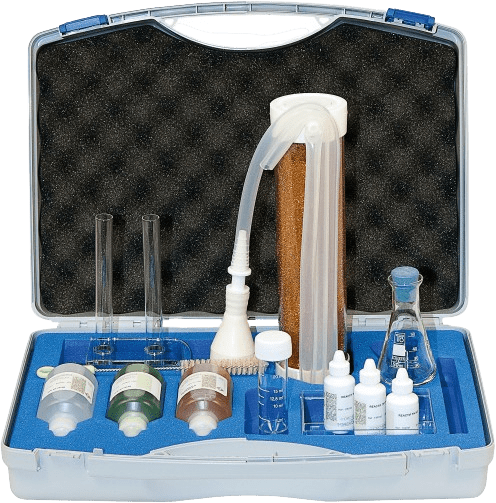
The case contains a mini softener and reagents for hardness, lime precipitation and soap tests. It is ideal for demonstrating the effectiveness of water softeners.
Learn moreClose reagent bottles immediately after use. Rinse the test container with distilled water only. Store the test kit in a cool (<25°C), dry place.
The consumption of the titrant solution depends on the concentration of the substance to be determined.
Barium, strontium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, iron, polyphosphate, aluminum, cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc can interfere with titration hardness values.
If there are sequestering products, such as polyphosphates, silicates, or tannins, hardness should be measured using the soap method. For further information on this method and the use of the reagents, please contact us.
Accurate interpretation of results is essential for making enlightened decisions and taking appropriate action to maintain the quality of the water and your equipment. Water hardness levels are classified as very soft (0 to 8°f), soft (8 to 15°f), medium hard (15 to 25°f), hard (25 to 35°f), and very hard water (> 35°f).
Hardness refers to the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions dissolved in water. These minerals are responsible for the buildup of lime. Total Hardness (TH) of water is expressed in French degrees (°f), where 1°F corresponds to 10 mg of CaCO₃/L

Measuring hardness is essential in assessing water quality. Hard water can lead to unwanted mineral deposits, affect the taste of drinks, and cause problems with household appliances. Soft water, on the other hand, can be corrosive and requires a delicate balance to prevent damage to your equipment.
Total hardness is the sum of carbonate and non-carbonate hardness. Carbonate hardness, due to calcium and magnesium bicarbonate, is sometimes called temporary hardness, and can be removed by boiling. Noncarbonate hardness, due to calcium and magnesium nitrates, chlorides, and sulfates, is also known as permanent hardness.
Hardness monitoring is vital in many fields, including the food industry, cooling systems, boilers, and power generation. Water of a specific quality, with controlled hardness concentrations, is essential to ensure optimal efficiency of machinery and to extend its useful life. Specific applications include preventing scaling in water heaters, managing boiler water to prevent corrosion, and optimizing the performance of softening systems to eliminate the adverse effects of hardness on industrial processes.
Hardness measures the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions, while alkalinity measures the ability of a solution to neutralize acids. Although related, hardness focuses on calcium and magnesium, while alkalinity includes the contribution of carbonate, bicarbonate, and hydroxide ions.
AQUALABO is a French manufacturer of instrumentation and chemical reagents for the control and analysis of water quality.
Contact us
© Aqualabo 2023 - All rights reserved