
Discover our rapid and reliable test kits to analyze water alkalinity. Available as kits and portable cases for occasional or domestic use, as well as large scale reagents used in laboratory burette methods for frequent testing in an industrial environment.
Alkalinity testing is essential in many areas, to reduce the toxicity of heavy metals and stabilize the pH in water treatment. However, extreme levels alter the taste of water and cause mineral deposits in industrial equipment. It is essential to accurately measure alkalinity.

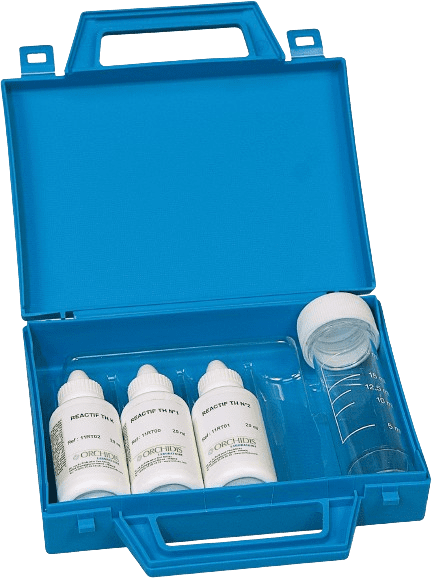
Discover our dropper alkalinity testers: a simple, fast, and reliable way to assess the alkalinity of water.
The dropper titration method causes the color of the sample to change at the equivalence point. The number of drops needed for the color to change represents the alkalinity concentration.
Choose our Alkalinity TA (AT Alkalimetric title) test kit, Alkalinity TAC (CAT Complete Alkalinity Title) test kit or combine both for a comprehensive analysis. The CMR-free indicator is also available.

CMR-free options available
100 tests
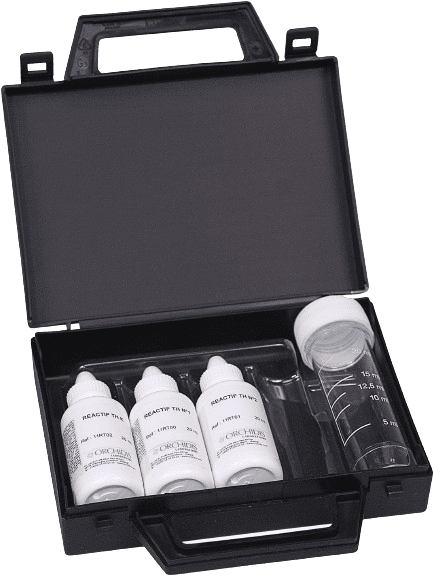
CMR-free options available
100 tests
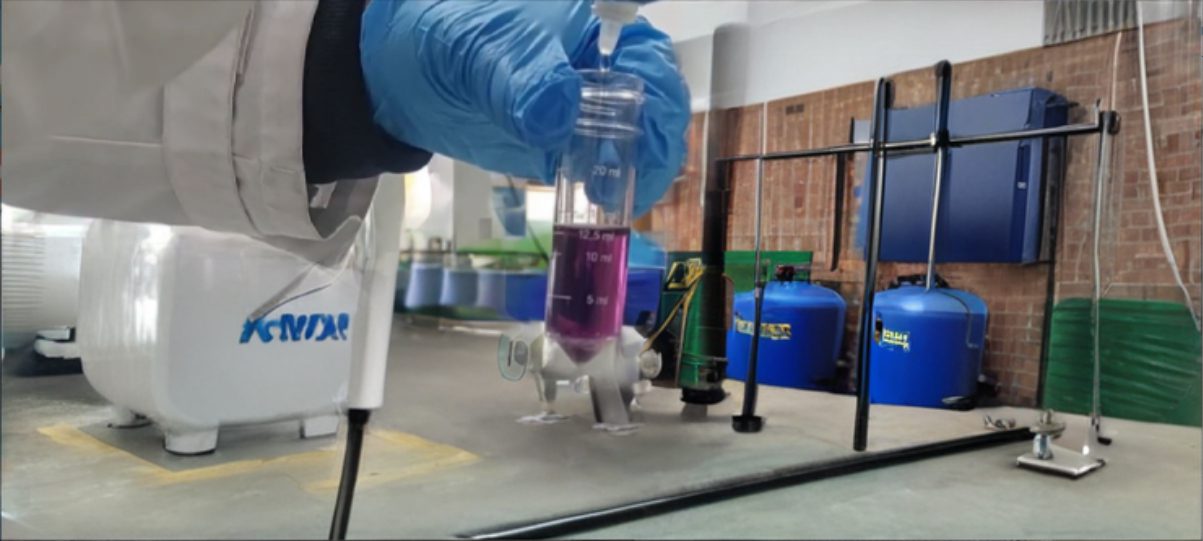
Burette dropper titration methods to determine the alkalinity of water offer a greater titrant solution storage capacity, thereby increasing the number of tests and speed with which they can be performed.
Explore our options: burette with a stand or burette with bottle pressure fill.
Choose our CMR-free TA (AT Alkalimetric title) and TAC (CAT Complete Alkalinity Title) methods for accurate analyses free of carcinogenic compounds.

Assess the alkalinity concentration by gradually adding the alkalinity liquor to the sample. Watch the color change from pink to colorless with the TA indicator (CMR-free) or TA phenolphthalein (CMR). For the TAC helianthine the color change is from yellow to orange and from blue-green to pale pink with the TAC reagent.
Learn moreClose reagent bottles immediately after use. Rinse the test vial with distilled water only. Store the kit in a cool (<25°C), dry place.
The consumption of the titrant solution depends on the concentration of the substance to be determined.
Dosage accuracy at pH 8.2 or 4.3 may be affected by buffer compounds such as salts from humic acids, phosphates, polyphosphates, citrates, and tartrates, in addition to carbonic acid and its salts. Furthermore, intrinsic coloration or turbidity in the water sample may make it difficult to see the color change clearly.
If the concentration of chlorine in the water sample exceeds 3.5 mg/L, the total alkalinity reagent method may be impeded by the development of a yellow-brown color. At this concentration, chlorine may discolor the normal the indicator, causing a bias in the interpretation of the result. Pretreating the sample is recommended to reduce this potential interference.
For specific advice on procedures and reagent use, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are here to ensure accurate results.
Accurate interpretation of results is essential to ensure water quality and optimal sustainability of your equipment.
The TAC or CAT level could ideally be between 8 and 14°F. A TAC or CAT level above 25°F may result in equipment scaling, deposits on the water line and high pH, while a TAC or CAT level below 6°F may result in harsh water and low pH.
The alkalinity of water is defined as its ability to neutralize acids through the action of dissolved bases and is therefore a measure of the buffering effect of water.
Measurement results are expressed in French degrees (°f), where 1°F corresponds to 10 mg of CaCO₃/L

Alkalinity TA (AT Alkalimetric title) or p-alkalinity is the alkalinity of water at a pH of 8.3, indicating the alkalinity relative to hydroxides and half the alkalinity relative to carbonates.
Total alkalinity TAC (CAT Complete Alkalinity Title), also known as m-alkalinity (methyl orange alkalinity) or acid demand for KS4.3, is used to determine the content of reactive basic compounds (hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates, etc.) up to a pH of about 4.3, thus including weak acids. In the case of natural water, it mainly represents the bicarbonate HCO₃⁻. In some highly polluted waters (wastewater), the CAT may also include weak organic acids (acetic, etc.). This may also occur in some very colorful natural waters (humic matter).
Alkalinity plays a fundamental role in maintaining pH stability. It is a critical parameter in assessing surface water quality and analyzing the corrosive behavior of water in general water treatment and wastewater treatment. Extreme levels alter the taste of water and cause mineral buildup in industrial plant.
Power plants: Optimizing heat transfer and reducing costs are essential in power plants. Maintaining the alkalinity of the cooling system preserves the protective oxide layer on the metal pipes. However, excessive alkalinity can lead to unwanted deposits.
Swimming pools: If the alkalinity of the water is too low, the pH can get out of control. If it is too high, there is a risk of scale deposits or cloudy pool water. The CAT of your water should be between 80 and 120 mg/l.
Anaerobic digestion: Alkalinity is essential to maintain optimal pH and ensure that the biological process is working properly.
Ammoniacal nitrogen removal: Constant monitoring of alkalinity is essential to ensure stable nitrification.
Drinking water treatment: Alkalinity acts as a pH buffer, promoting effective coagulation and softening, while controlling corrosivity in the distribution system.
Drinks manufacturing: Alkalinity monitoring is essential to ensure the quality of drinks, preventing spoilage due to incorrect alkalinity.
AQUALABO is a French manufacturer of instrumentation and chemical reagents for the control and analysis of water quality.
Contact us
© Aqualabo 2023 - All rights reserved